PURPOSE
The purpose of this experiment was to determine the effect of electrode combinations on the voltage of a galvanic cell.
I became interested in this idea when I was listening to my CD player and wondered how the battery made energy for the CD player to use.
The information gained from this experiment would help all wet cell battery users by finding metals with more electrical output. Almost everyone in our society uses these batteries.
HYPOTHESIS
My hypothesis
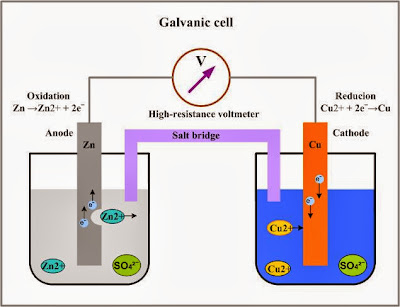
was that a zinc anode and copper cathode would create the most voltage output.
I based my hypothesis on an article in the Hutchison Dictionary of Science that stated, “The first galvanic battery that was made by Luigi Galvani used zinc as a anode and copper as a cathode which still proves to be efficient.”
EXPERIMENT DESIGN
The constants
in this study were:
- The size of the metal electrod
- Amount of electrolyte
- Size of beaker
- Voltmeter
- Temperature
The manipulated variable was the combinations I use as electrodes to create a galvanic cell.
The responding variable was the electrical output.
To measure the responding variable I used a voltmeter to measure the galvanic cell’s electrical potential.
QUANTITY
|
ITEM
DESCRIPTION
|
1
|
Voltmeter
|
1
|
Glass Beaker
|
2
|
Zinc
2cm x 12cm
|
2
|
Copper
2cm x 12cm
|
2
|
Lead
2cm x 12cm
|
200ml
|
Copper
Nitrate
|
200ml
|
Zinc Nitrate
|
200ml
|
Lead Nitrate
|
3
|
Porous cups
|
1. Clean the
copper, lead and zinc strips before starting the experiment. Sand with a fine
grade sand paper to take off the outside coating.
2. Place 50ml of the matching electrolyte with the metal strip you’re using in the beaker.
3. Take another electrolyte and add 50ml to the porous and add the matching metal.
4. Attach the voltmeter’s ends to the two metals.
5. Put the porous cup in the beaker.
6. Immediately take volt recordings in mini volts.
7. Repeat steps 2-5 3 times.
8. After conducting all of the experiment clean up all of the mess from conducting the experiment.
RESULTS
The original
purpose of this experiment was to determine the effect of electrode
combinations on the voltage of a galvanic cell.
The results of the experiment were the lead-copper test created the most potential at 481.2 mv. The lead-zinc test created 106.4 mv. The zinc-copper test created 82.3 mv.
My hypothesis was that a zinc anode and copper cathode would
create the most voltage output.
The results indicate that this hypothesis should be rejected for
the lead-copper galvanic cell created more energy.
Because of the results of this experiment, I wonder if using
sulfates or carbonates instead of nitrates as electrolytes would change the
electrical output. Another thing that could be changed is the temperature. I
did this experiment at room temperature (20∞C). You could do it at 0∞C
(freezing) or at about 40∞C, which is like a hot summer day.
If I were to conduct this project again I would try to use more anode cathode combinations. I would conduct more trials. I would use a voltmeter that was very precise and accurate below one volt. I would repeat the entire experiment, using fresh electrolytes and electrodes. I would also soak the porous cups for a few hours before the experiment.
Researched
by Derek L.






0 comments:
Post a Comment